Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 09 janeiro 2025
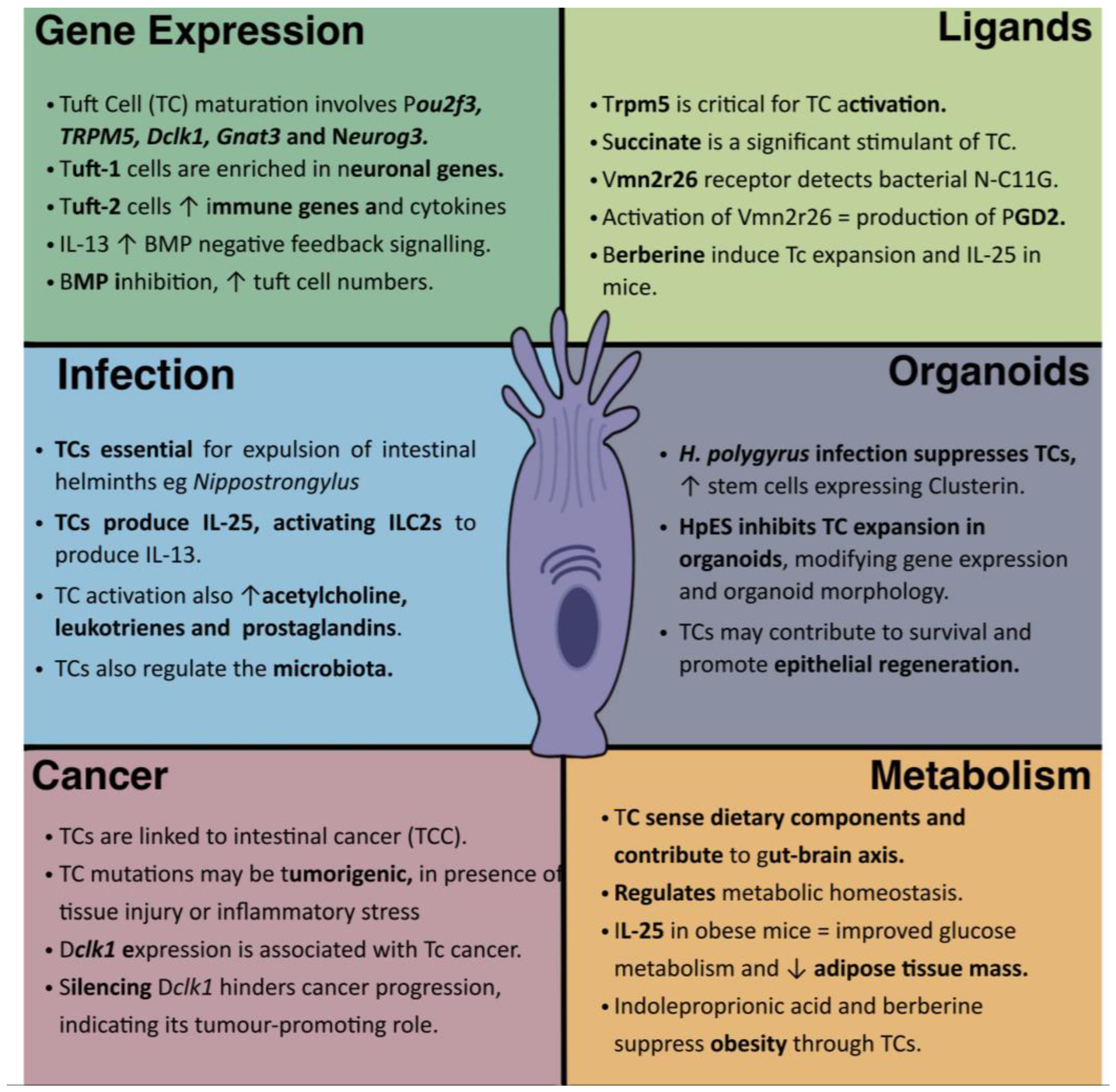
Tuft cells have recently emerged as the focus of intense interest following the discovery of their chemosensory role in the intestinal tract, and their ability to activate Type 2 immune responses to helminth parasites. Moreover, they populate a wide range of mucosal tissues and are intimately connected to immune and neuronal cells, either directly or through the release of pharmacologically active mediators. They are now recognised to fulfil both homeostatic roles, in metabolism and tissue integrity, as well as acting as the first sensors of parasite infection, immunity to which is lost in their absence. In this review we focus primarily on the importance of tuft cells in the intestinal niche, but also link to their more generalised physiological role and discuss their potential as targets for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders.

Five-Year Outcomes for Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas with CAR T-Cell Therapy

Cell-free Fetal DNA — A Trigger for Parturition
Cells, Free Full-Text
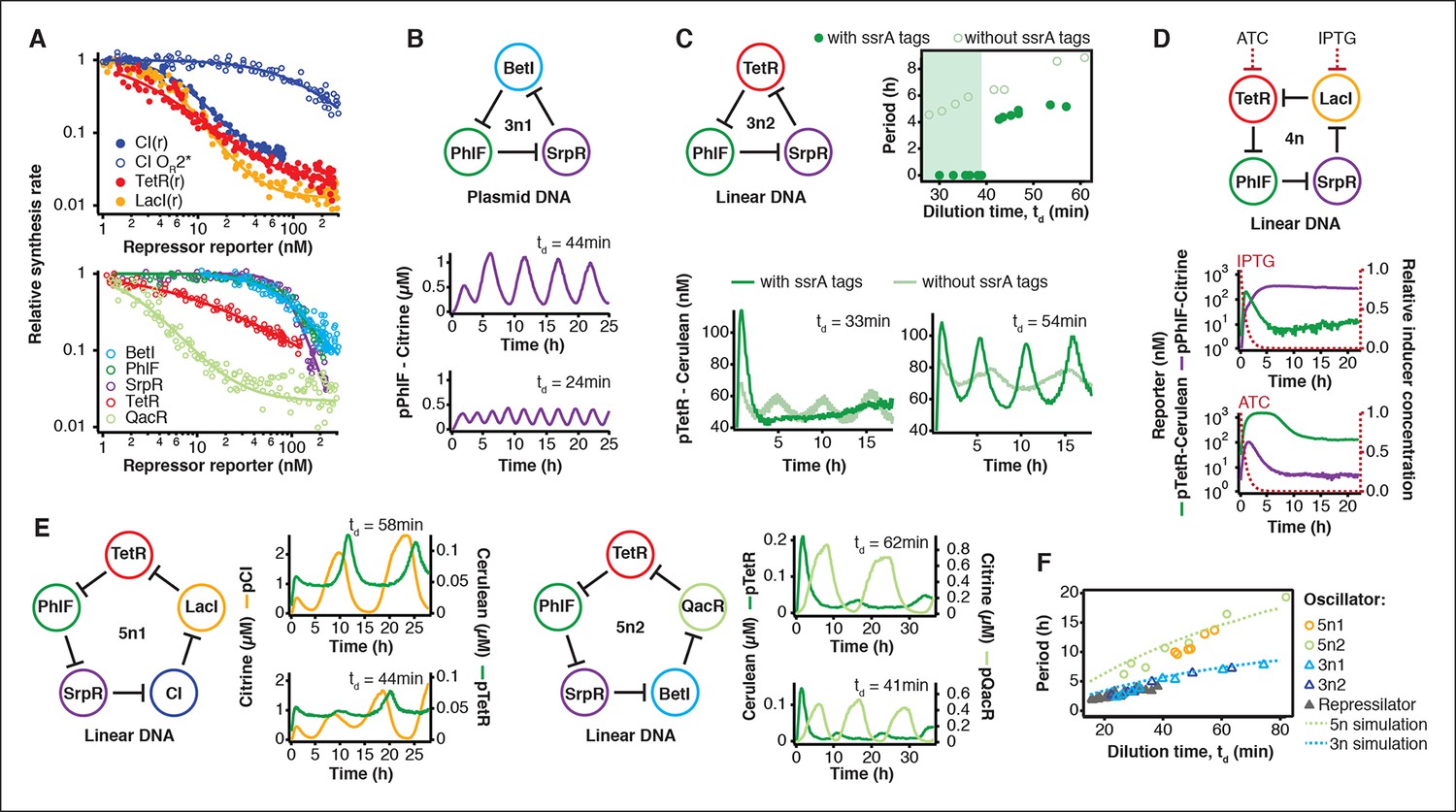
Rapid cell-free forward engineering of novel genetic ring oscillators

Cells, Free Full-Text
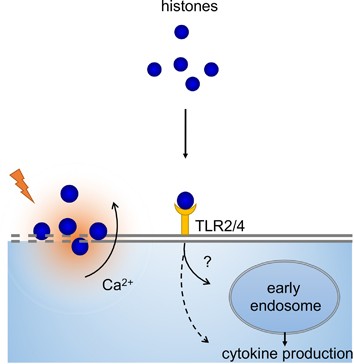
Extracellular histones, cell-free DNA, or nucleosomes: differences in immunostimulation
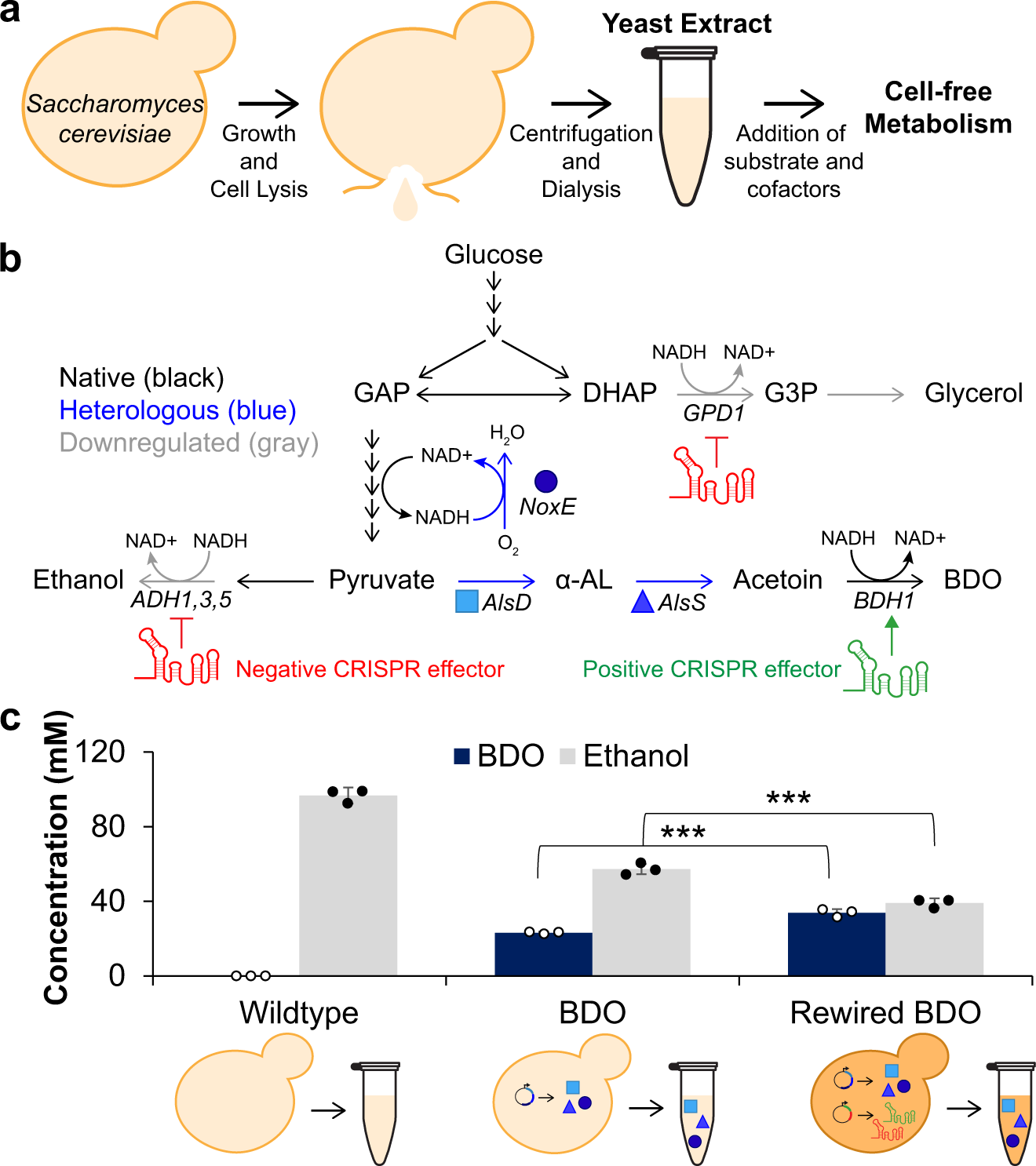
An integrated in vivo/in vitro framework to enhance cell-free biosynthesis with metabolically rewired yeast extracts
from Flow Cytometry to Cytomics, Page 2
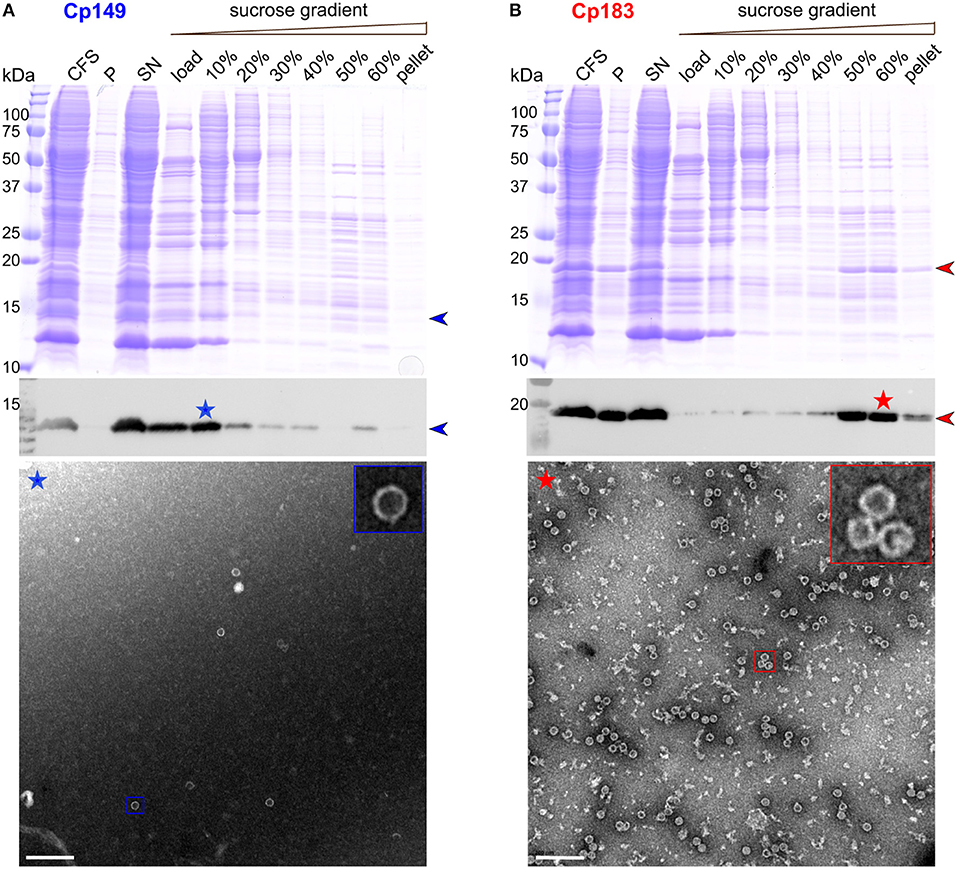
Frontiers Combining Cell-Free Protein Synthesis and NMR Into a Tool to Study Capsid Assembly Modulation
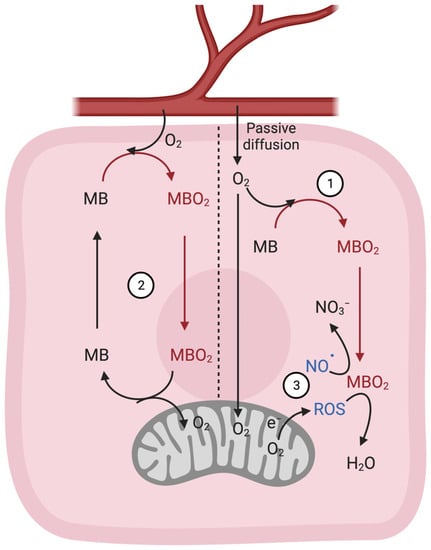
Nt Novo Cella Get File - Colaboratory
An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.
Cells, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 Welcome to League of Legends: Wild Rift09 janeiro 2025
Welcome to League of Legends: Wild Rift09 janeiro 2025 -
 Wild Rift News September 9, 202209 janeiro 2025
Wild Rift News September 9, 202209 janeiro 2025 -
 Tormented Souls : Ui Entertainment: Video Games09 janeiro 2025
Tormented Souls : Ui Entertainment: Video Games09 janeiro 2025 -
 Archuu 5.45in Smartphone, Rino4 Pro Face Unlock Intelligent Unlocked Cell Phones Dual Cards Dual Standby Smartphone 1+8G Full Screen Smartphone09 janeiro 2025
Archuu 5.45in Smartphone, Rino4 Pro Face Unlock Intelligent Unlocked Cell Phones Dual Cards Dual Standby Smartphone 1+8G Full Screen Smartphone09 janeiro 2025 -
 forsen has been moved to a new Cell : r/LivestreamFail09 janeiro 2025
forsen has been moved to a new Cell : r/LivestreamFail09 janeiro 2025 -
 5 Anticipated Games We Are Surprised Have Not Come to Nintendo Switch Yet - EssentiallySports09 janeiro 2025
5 Anticipated Games We Are Surprised Have Not Come to Nintendo Switch Yet - EssentiallySports09 janeiro 2025 -
 iPhone XR Dabbing Unicorn Russia Ice Hockey Fans Jersey Winter Sports Case09 janeiro 2025
iPhone XR Dabbing Unicorn Russia Ice Hockey Fans Jersey Winter Sports Case09 janeiro 2025 -
![Splinter Cell: Complete Stealth Walkthrough, Part 4 Oil RIg [XBOX ONE X]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/6Eou4MfwJNA/hq720.jpg?sqp=-oaymwEhCK4FEIIDSFryq4qpAxMIARUAAAAAGAElAADIQj0AgKJD&rs=AOn4CLC-xyHNcB-H_zDiFI4aCQIA8aT6aw) Splinter Cell: Complete Stealth Walkthrough, Part 4 Oil RIg [XBOX ONE X]09 janeiro 2025
Splinter Cell: Complete Stealth Walkthrough, Part 4 Oil RIg [XBOX ONE X]09 janeiro 2025 -
 20XX is a procedural Mega Man X, and it owns09 janeiro 2025
20XX is a procedural Mega Man X, and it owns09 janeiro 2025 -
 Lot Of 10 Original Xbox Games Clean & Tested09 janeiro 2025
Lot Of 10 Original Xbox Games Clean & Tested09 janeiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 USED) Manga Tokyo Ravens: Sword of Song vol.2 (東京レイヴンズ Sword of Song(2) (ライバルKC)) / Kuze Ran09 janeiro 2025
USED) Manga Tokyo Ravens: Sword of Song vol.2 (東京レイヴンズ Sword of Song(2) (ライバルKC)) / Kuze Ran09 janeiro 2025 -
 Black 2 & White 2 arc (Adventures) - Bulbapedia, the community09 janeiro 2025
Black 2 & White 2 arc (Adventures) - Bulbapedia, the community09 janeiro 2025 -
![Mystery Scrap Box - 10 lb [MYSTERYBOX] - $49.95](https://burlapfabric.com/images/mysterybx.jpg) Mystery Scrap Box - 10 lb [MYSTERYBOX] - $49.9509 janeiro 2025
Mystery Scrap Box - 10 lb [MYSTERYBOX] - $49.9509 janeiro 2025 -
 Pablo Acosta09 janeiro 2025
Pablo Acosta09 janeiro 2025 -
 Tokyo Revengers' confirma la fecha de estreno de su temporada 2 en Disney+: el anime de pandilleros nos contará su historia navideña más tarde de lo que nos habría gustado09 janeiro 2025
Tokyo Revengers' confirma la fecha de estreno de su temporada 2 en Disney+: el anime de pandilleros nos contará su historia navideña más tarde de lo que nos habría gustado09 janeiro 2025 -
 KIRBY PATTERNS Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra Case09 janeiro 2025
KIRBY PATTERNS Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra Case09 janeiro 2025 -
 Project Slayer Itens, Espadas, Roupas e - Roblox - Project Slayers - GGMAX09 janeiro 2025
Project Slayer Itens, Espadas, Roupas e - Roblox - Project Slayers - GGMAX09 janeiro 2025 -
 SHINY Lucario & MYTHICAL Darkrai Mystery Gift Codes ▻ Pokemon Scarlet & Violet09 janeiro 2025
SHINY Lucario & MYTHICAL Darkrai Mystery Gift Codes ▻ Pokemon Scarlet & Violet09 janeiro 2025 -
 Garfo de Mesa Aço Inox Angra Hércules 1377-00209 janeiro 2025
Garfo de Mesa Aço Inox Angra Hércules 1377-00209 janeiro 2025 -
 28 melhores filmes de guerra de todos os tempos - Cultura Genial09 janeiro 2025
28 melhores filmes de guerra de todos os tempos - Cultura Genial09 janeiro 2025