PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 dezembro 2024
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/76d00455660f8d0dfa42fcd70278635b6c0e6ff5/1-Figure1-1.png)
A typical six-month-old girl with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome was presented with typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate. Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (RTS) was first described by Michail et al[1] and subsequently by Rubinstein and Taybi[2]. We present a typical six-month-old girl with RTS. Her mother had ovarian cancer and polyhydramnios during the pregnancy. Parents are closely related. There were frequent respiratory infections resulting in two hospital admissions. Physical examination revealed typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate (Fig. 1). A history of increased tearing was compatible with nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Other features include general hypotonia with delayed developmental milestones, short and broad thumbs and toes (Fig. 1). Chest x-ray showed cardiomegaly (Fig. 2). She had normal karyotype.
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41372-019-0506-7/MediaObjects/41372_2019_506_Fig1_HTML.png)
Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: is early transcatheter closure a paradigm shift?
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.ahajournals.org/cms/asset/a6672ae3-8d0f-4b81-a312-1cbfe4d5a5c3/jah37672-fig-0004.png)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A Contemporary Perspective for the Pediatric and Adult Cardiac Care Provider
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdanew27-230728061043-255bae9f/85/pdapptx-1-320.jpg?cb=1690524966)
PDA.pptx
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://static.cambridge.org/binary/version/id/urn:cambridge.org:id:binary:20210407112525727-0240:9781108668736:46551fig59_1.png?pub-status=live)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (Chapter 59) - Case Studies in Pediatric Anesthesia
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Patrick-Mcnamara-14/publication/324968903/figure/fig9/AS:963235951943683@1606664755233/A-and-B-Angiographic-still-frames-in-lateral-projection-of-the-patent-ductus_Q320.jpg)
PDF) Patent ductus arteriosus: The physiology of transition
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://i1.rgstatic.net/ii/profile.image/926912121675782-1598004479904_Q64/Ehsan-Aghaei-Moghadam.jpg)
PDF) Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/lw685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41598-019-52936-6/MediaObjects/41598_2019_52936_Fig4_HTML.png)
Characteristics of Patent Ductus Arteriosus in Congenital Rubella Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1186%2F1750-1172-4-17/MediaObjects/13023_2008_Article_151_Fig1_HTML.jpg)
Patent arterial duct, Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1058981319301821-gr3.jpg)
Transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus in a tiniest baby – 510 grams - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/e26024cbcda91686a23ad5772202713ea6665ad7/3-Figure3-1.png)
PDF] Patent ductus arteriosus closure using an Amplatzer ventricular septal defect closure device in adulthood
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/e26024cbcda91686a23ad5772202713ea6665ad7/2-Figure1-1.png)
PDF] Patent ductus arteriosus closure using an Amplatzer ventricular septal defect closure device in adulthood
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1186%2F1750-1172-4-17/MediaObjects/13023_2008_Article_151_Fig5_HTML.jpg)
Patent arterial duct, Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases
Recomendado para você
-
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: Behavior31 dezembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: Behavior31 dezembro 2024 -
 Facial features of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome31 dezembro 2024
Facial features of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome31 dezembro 2024 -
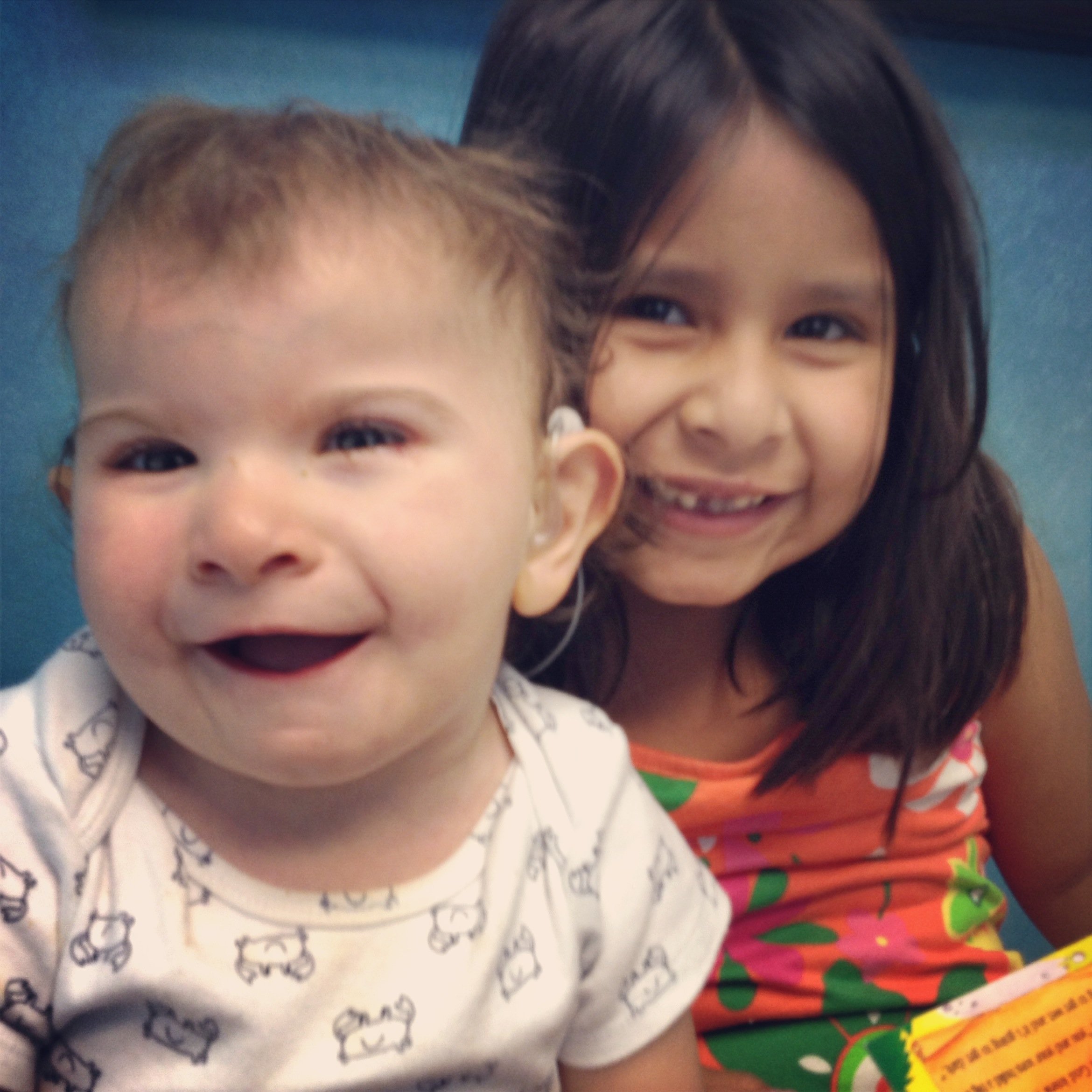 Born with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RTS), Braxton and Family are31 dezembro 2024
Born with Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome (RTS), Braxton and Family are31 dezembro 2024 -
 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (broad thumb-hallux syndrome)31 dezembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (broad thumb-hallux syndrome)31 dezembro 2024 -
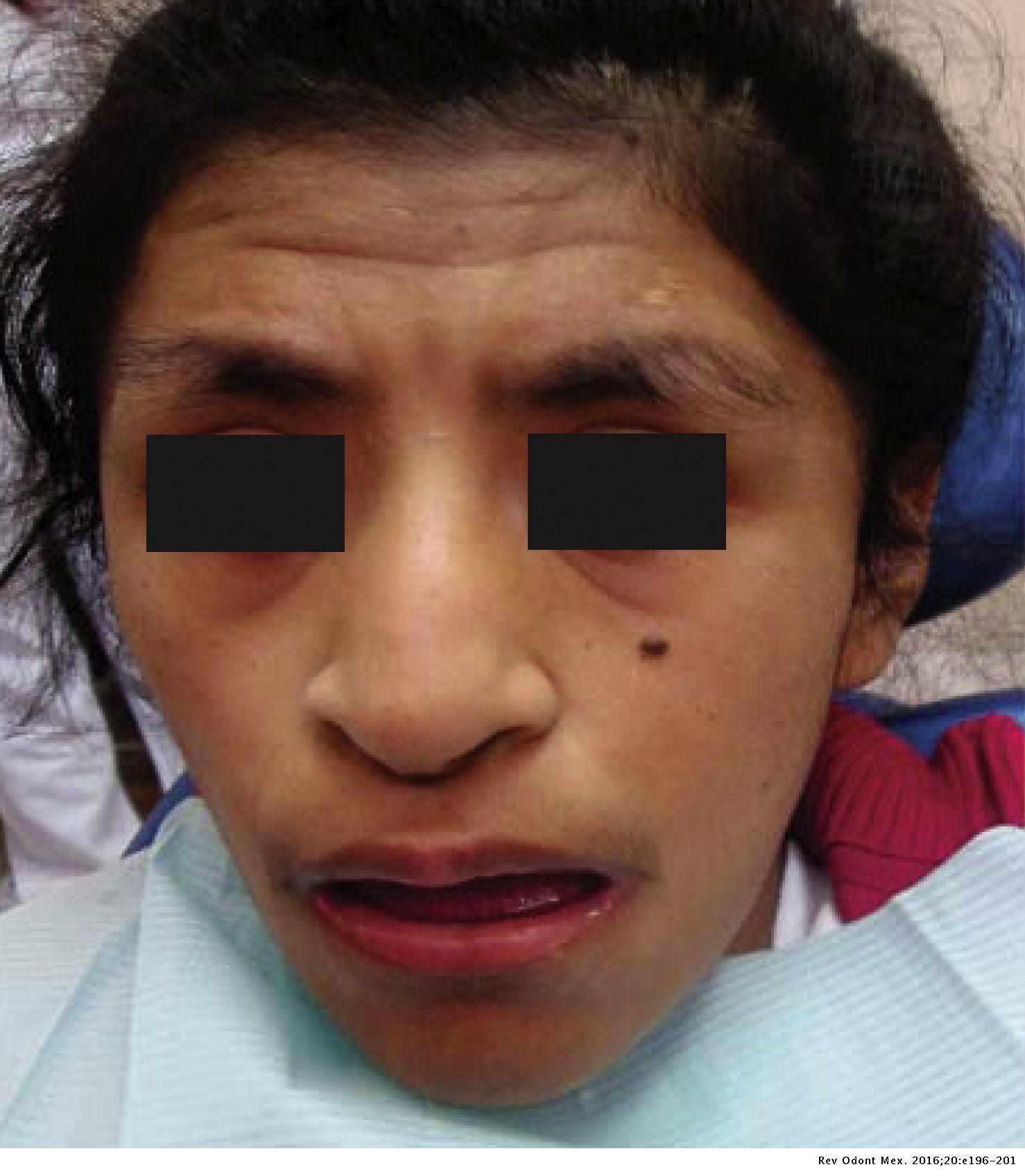 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, medical and dental care for special needs patients: Clinical case report31 dezembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, medical and dental care for special needs patients: Clinical case report31 dezembro 2024 -
 El Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taibi - Hospital Cabral y Baez31 dezembro 2024
El Síndrome de Rubinstein-Taibi - Hospital Cabral y Baez31 dezembro 2024 -
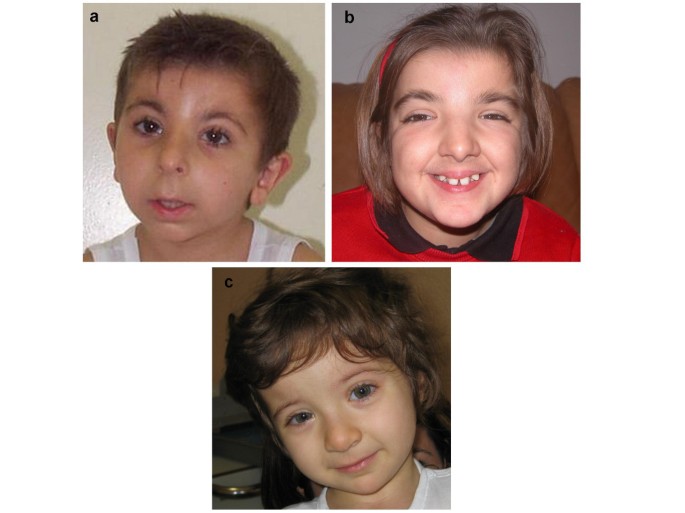 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: spectrum of CREBBP mutations in Italian patients, BMC Medical Genetics31 dezembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: spectrum of CREBBP mutations in Italian patients, BMC Medical Genetics31 dezembro 2024 -
 Revista rst edição 4REVISTA RST-SINDROME RUBINSTEIN TAYBI by elaine paoli - Issuu31 dezembro 2024
Revista rst edição 4REVISTA RST-SINDROME RUBINSTEIN TAYBI by elaine paoli - Issuu31 dezembro 2024 -
Asociación Española Síndrome de Rubinstein Taybi - “La mejor31 dezembro 2024
-
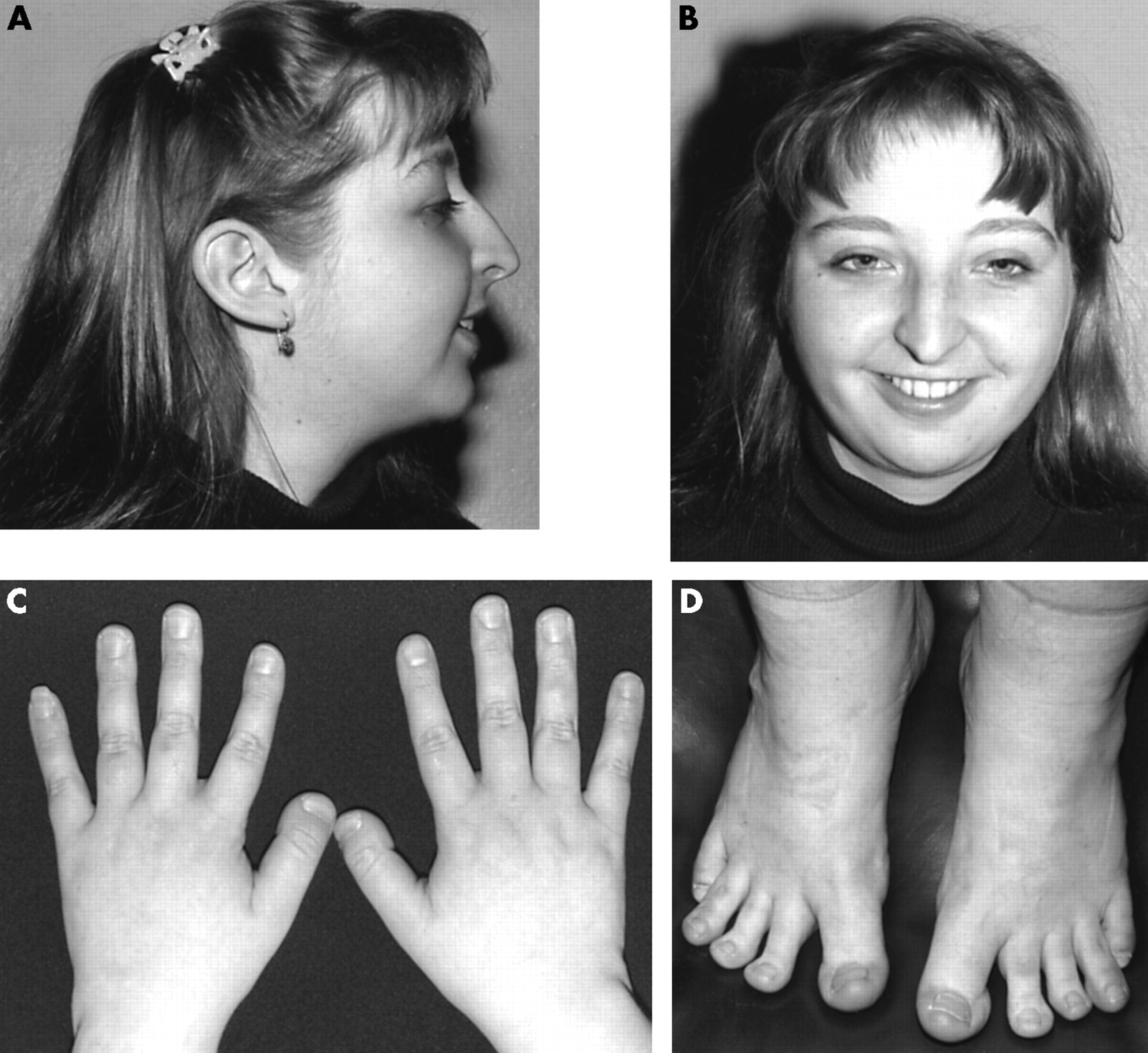 Molecular studies in 10 cases of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, including a mild variant showing a missense mutation in codon 1175 of CREBBP31 dezembro 2024
Molecular studies in 10 cases of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, including a mild variant showing a missense mutation in codon 1175 of CREBBP31 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
Manga de hanyo no yashahime cap 2 - Moroha Higurashi 24331 dezembro 2024
-
 How to Download and Install Gameloop Android Emulator on Windows31 dezembro 2024
How to Download and Install Gameloop Android Emulator on Windows31 dezembro 2024 -
 The Electrical Room, DOORS Wiki31 dezembro 2024
The Electrical Room, DOORS Wiki31 dezembro 2024 -
 Chivalry II é confirmado para PS4 e PS5; haverá cross-play entre todas as plataformas - PSX Brasil31 dezembro 2024
Chivalry II é confirmado para PS4 e PS5; haverá cross-play entre todas as plataformas - PSX Brasil31 dezembro 2024 -
Dead.Shark - Fundy and 5up Plushie fan art 2/2 #5up31 dezembro 2024
-
Coleção 100 Carrinhos Usados - Hot Wheels, Carros, Mcqueen, Blaze, Playmobil, Brinquedo para Bebês Mattel Usado 8867044931 dezembro 2024
-
VK MR OWII #fyp #foryoupage #freefire #gareenafreefire #baba_4u31 dezembro 2024
-
1001 Jogos em Oferta31 dezembro 2024
-
 PASSIONE AZZURRA: 31/1/2017, TORNEO 1ª “C” 2016/2017: SPORTIVO ITALIANO-PRETEMPORADA. R.CARUSO LOMBARDI: “VAMOS A INTENTAR PELEAR EL ASCENSO”.31 dezembro 2024
PASSIONE AZZURRA: 31/1/2017, TORNEO 1ª “C” 2016/2017: SPORTIVO ITALIANO-PRETEMPORADA. R.CARUSO LOMBARDI: “VAMOS A INTENTAR PELEAR EL ASCENSO”.31 dezembro 2024 -
 Hunter X Hunter Men's and Big Men's Short Sleeve Graphic Tee31 dezembro 2024
Hunter X Hunter Men's and Big Men's Short Sleeve Graphic Tee31 dezembro 2024





