Performance of Brain-Injured versus Non-Brain-Injured Individuals on Three Versions of the Category Test - Page 120 - UNT Digital Library
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 10 novembro 2024
To date, no research exists examining criterion-related validity of alternate, computerized forms of the Category Test. The intent of this study was to address criterion-related validity of three full forms of the Category Test. In that, the goal was to examine equivalency of each version in their ability to differentiate brain-injured from non-brain-injured individuals. Forty-nine (N = 49) healthy adults and 45 (N = 45) brain-injured adults were tested using three versions of the Category Test, the BDI, and the WAIS-R NI. ANOVA indicated no significant differences between versions of the Category Test or an interaction between Category Test version and group membership on the total error score. MANOVA performed between versions of the Category Test and Subtest error scores indicated significant differences between versions on Subtest 3 and Subtest 6. Group membership (brain-injured v. non-brain-injured) produced a significant main effect on all subtests of the Category Test except Subtest 2. Several exploratory analyses were performed examining the relationship between neuropsychological impairment, group membership based on Category Test error scores, and the WAIS-R NI. Clinical applications, such as the use of serial testing to index neurorehabilitation gains, were discussed.
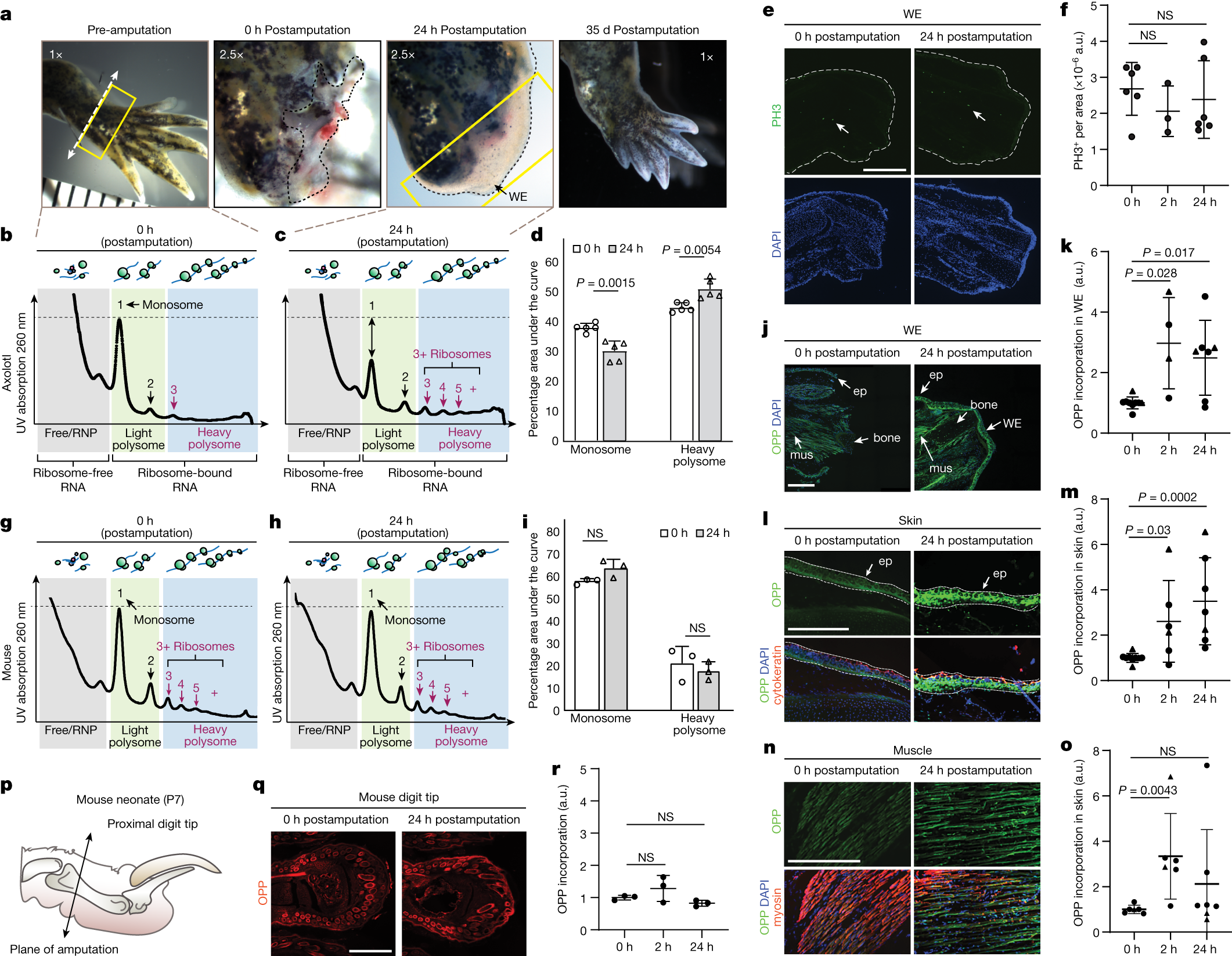
Evolutionarily divergent mTOR remodels translatome for tissue
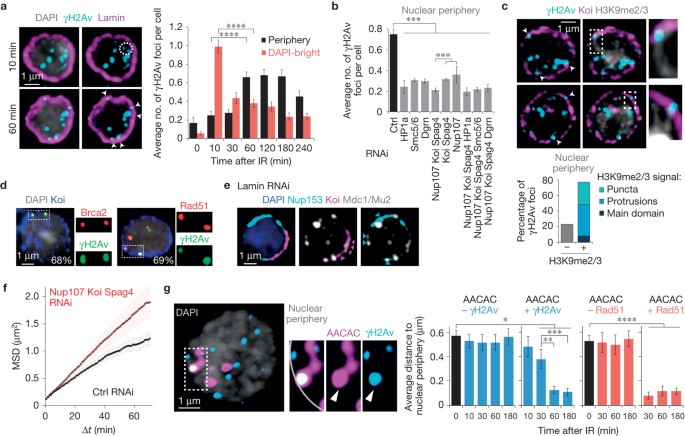
Heterochromatic breaks move to the nuclear periphery to continue

Preclinical studies of transcranial photobiomodulation in the

PDF) NEUROTRAUMA: FROM EMERGENCY ROOM TO BACK TO DAY-BY-DAY LIFE

Agronomy Announcements

Interface, VOL. 32, No. 1, Spring 2023 by The Electrochemical
Cells October-1 2022 - Browse Articles
JCM October-1 2023 - Browse Articles

Propeller Ed Kit Labs Fundamentals Datasheet by Parallax Inc

PDF) Intraventricular Hemorrhage and White Matter Injury in

PDF) Compensatory-reserve-weighted intracranial pressure versus

Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Recomendado para você
-
 BRAIN TEST NÍVEL 367 EM PORTUGUÊS10 novembro 2024
BRAIN TEST NÍVEL 367 EM PORTUGUÊS10 novembro 2024 -
 Brain Test Level 367 answer/solution. #shorts #braintest10 novembro 2024
Brain Test Level 367 answer/solution. #shorts #braintest10 novembro 2024 -
 Kunci Jawaban Brain Test Level 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370: Saatnya Mencari Cuan - Tribunbengkulu.com10 novembro 2024
Kunci Jawaban Brain Test Level 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370: Saatnya Mencari Cuan - Tribunbengkulu.com10 novembro 2024 -
 Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson's Disease10 novembro 2024
Deep-Brain Stimulation for Parkinson's Disease10 novembro 2024 -
 Brain Test: Tricky Puzzles Answers for All Levels - Page 37 of 46 - Level Winner10 novembro 2024
Brain Test: Tricky Puzzles Answers for All Levels - Page 37 of 46 - Level Winner10 novembro 2024 -
UTRGV Office For Sustainability - The Rio Grande Valley - Society For Neuroscience- Chapter (RGV-SFN-C) is organizing several events in its mission of promoting: Outreach, Education, Research in the Neuroscience10 novembro 2024
-
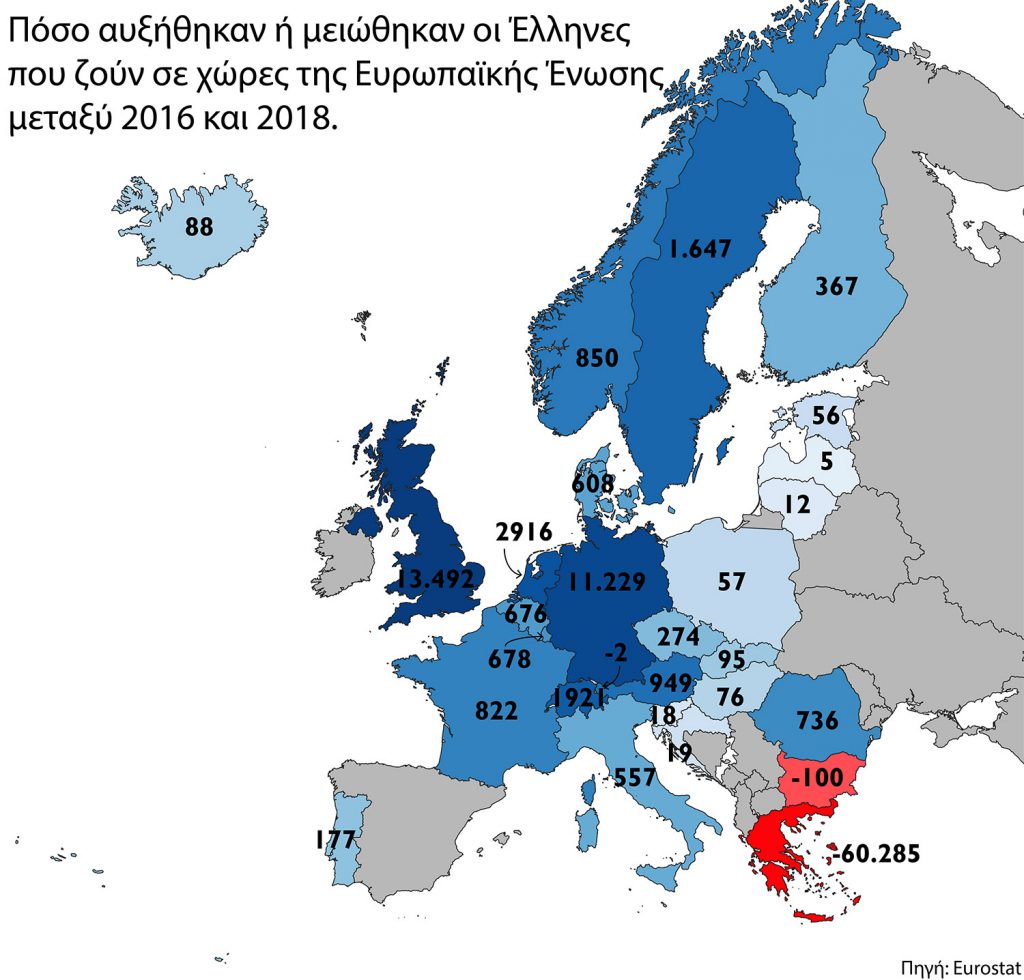 Από το Brain Drain στο Brain Gain: Έτσι μπορεί να αναστραφεί το φαινόμενο (fortunegreece.gr)10 novembro 2024
Από το Brain Drain στο Brain Gain: Έτσι μπορεί να αναστραφεί το φαινόμενο (fortunegreece.gr)10 novembro 2024 -
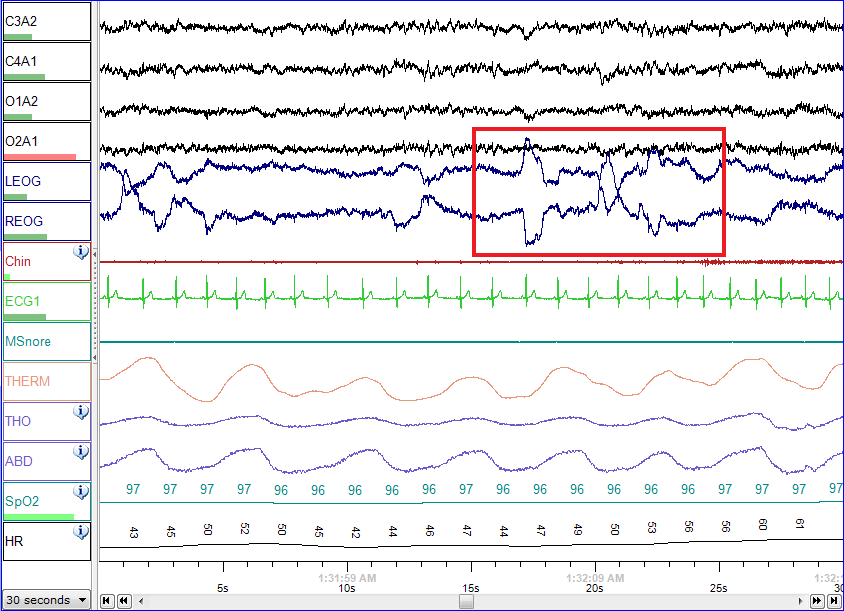 Polysomnography - Wikipedia10 novembro 2024
Polysomnography - Wikipedia10 novembro 2024 -
 Neuroimaging and deep learning for brain stroke detection - A review of recent advancements and future prospects - ScienceDirect10 novembro 2024
Neuroimaging and deep learning for brain stroke detection - A review of recent advancements and future prospects - ScienceDirect10 novembro 2024 -
 Gut Microbiome–Brain Alliance: A Landscape View into Mental and10 novembro 2024
Gut Microbiome–Brain Alliance: A Landscape View into Mental and10 novembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 O maior teste de Transformers como franquia de filmes acontecerá em 1 ano10 novembro 2024
O maior teste de Transformers como franquia de filmes acontecerá em 1 ano10 novembro 2024 -
 Orden recomendado a seguir por el mapa de Pokémon Escarlata y10 novembro 2024
Orden recomendado a seguir por el mapa de Pokémon Escarlata y10 novembro 2024 -
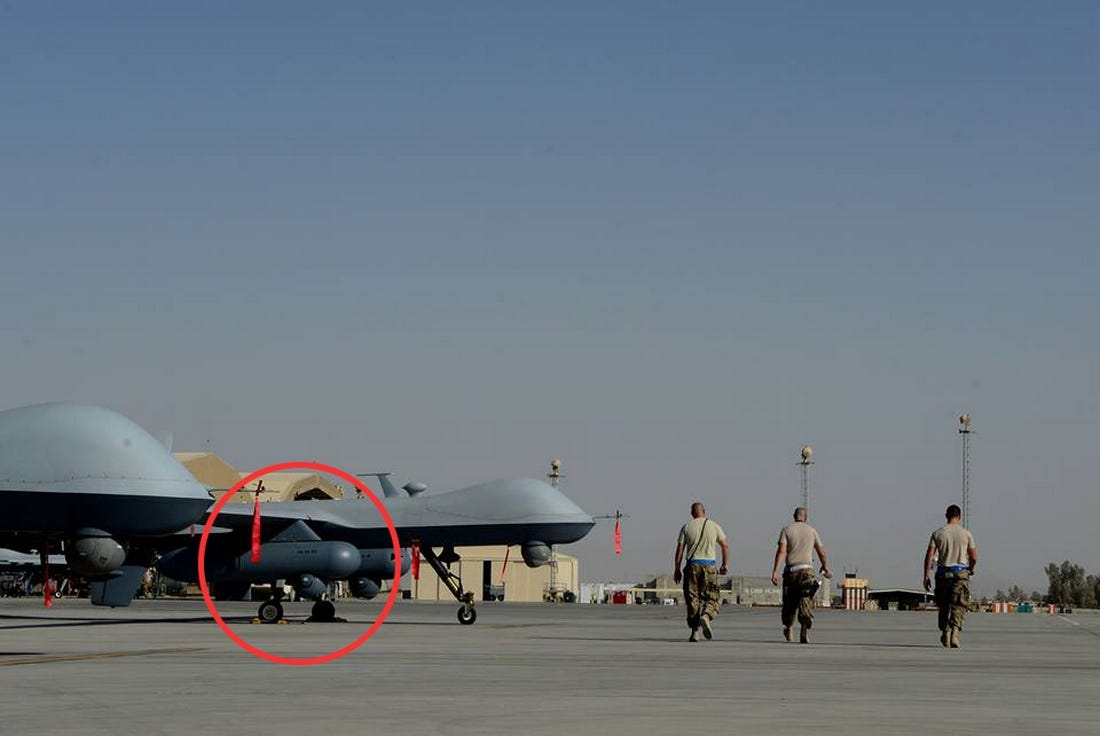 This New Drone Sensor Can Scan a Whole City at Once, by War Is Boring, War Is Boring10 novembro 2024
This New Drone Sensor Can Scan a Whole City at Once, by War Is Boring, War Is Boring10 novembro 2024 -
 Good Girl - Apple Music10 novembro 2024
Good Girl - Apple Music10 novembro 2024 -
 Beating snake game double snake mode!10 novembro 2024
Beating snake game double snake mode!10 novembro 2024 -
 Speed Drawing - Naruto & Sasuke (NARUTO CLASSIC)10 novembro 2024
Speed Drawing - Naruto & Sasuke (NARUTO CLASSIC)10 novembro 2024 -
 Brinquedo De Montar Mega Construx Pokémon Raichu 73 Peças em Promoção na Americanas10 novembro 2024
Brinquedo De Montar Mega Construx Pokémon Raichu 73 Peças em Promoção na Americanas10 novembro 2024 -
 Polyphony Digital says a PC version of Gran Turismo 7 isn't in development10 novembro 2024
Polyphony Digital says a PC version of Gran Turismo 7 isn't in development10 novembro 2024 -
 Nintendo domina as vendas de jogos no Japão há 18 anos10 novembro 2024
Nintendo domina as vendas de jogos no Japão há 18 anos10 novembro 2024 -
 Comprar Rayman Legends: Definitve Edition Switch Nintendo Eshop10 novembro 2024
Comprar Rayman Legends: Definitve Edition Switch Nintendo Eshop10 novembro 2024
