Solved Theorem 8.35 (Lagrange's Four-Square Theorem) If n is
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 31 dezembro 2024

Answer to Solved Theorem 8.35 (Lagrange's Four-Square Theorem) If n is
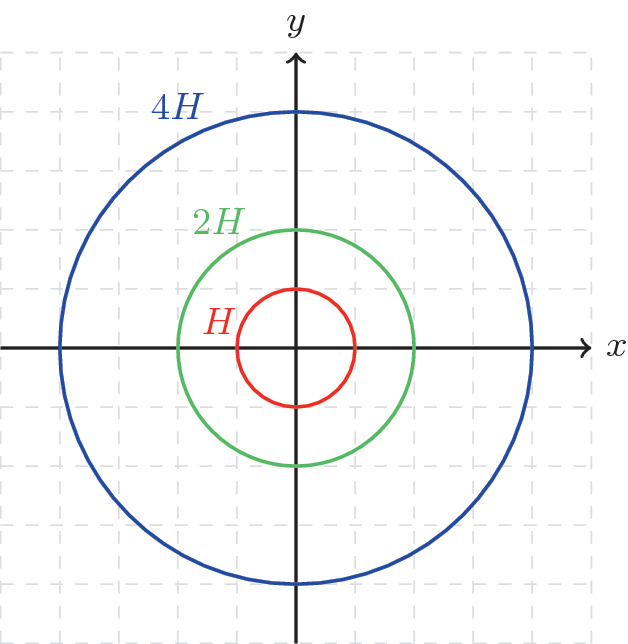
Cosets of Subgroups and Lagrange's Theorem

Numerical Solution of Partial Differential Equations - Gordon Everstine

MathType - Lagrange's four-square theorem states that every natural number can be represented as the sum of four integer squares. Proved by Joseph Louis #Lagrange in 1770, it can be regarded as
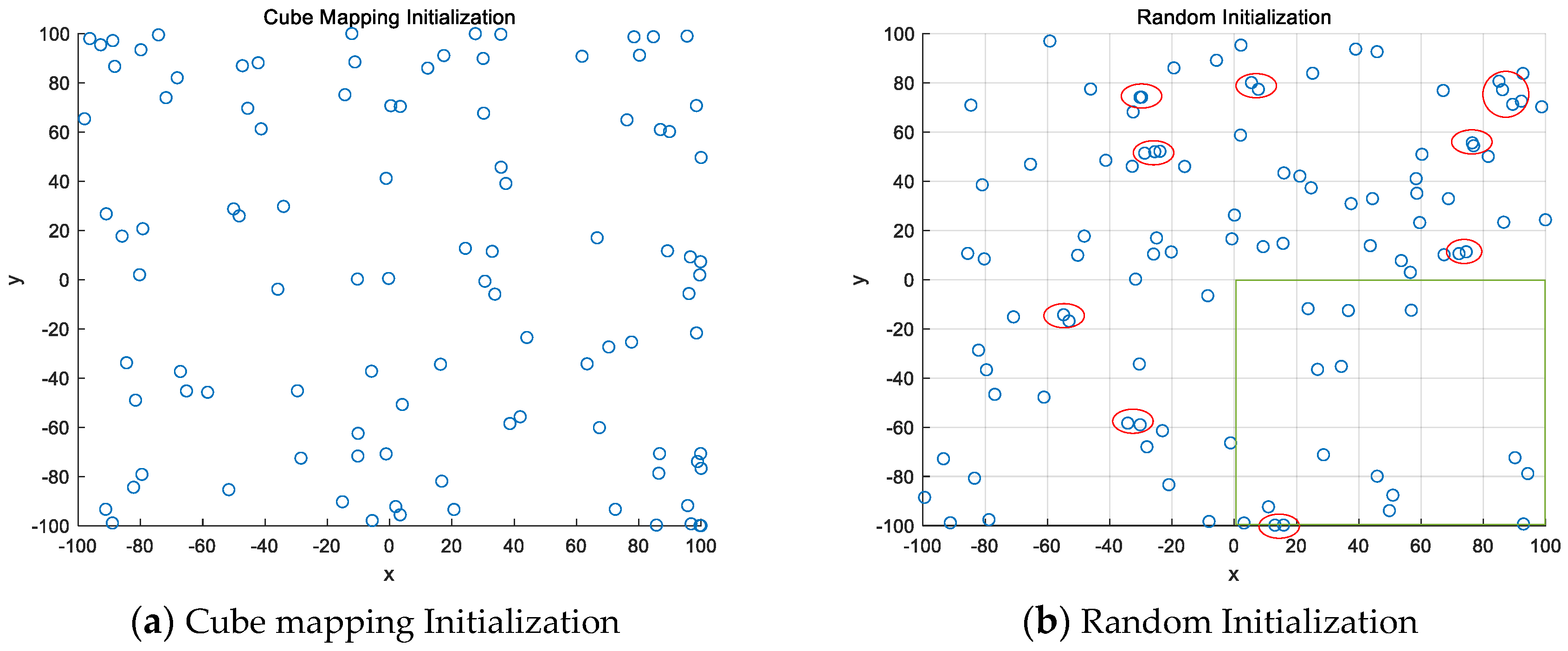
Axioms, Free Full-Text

Abstract Algebra
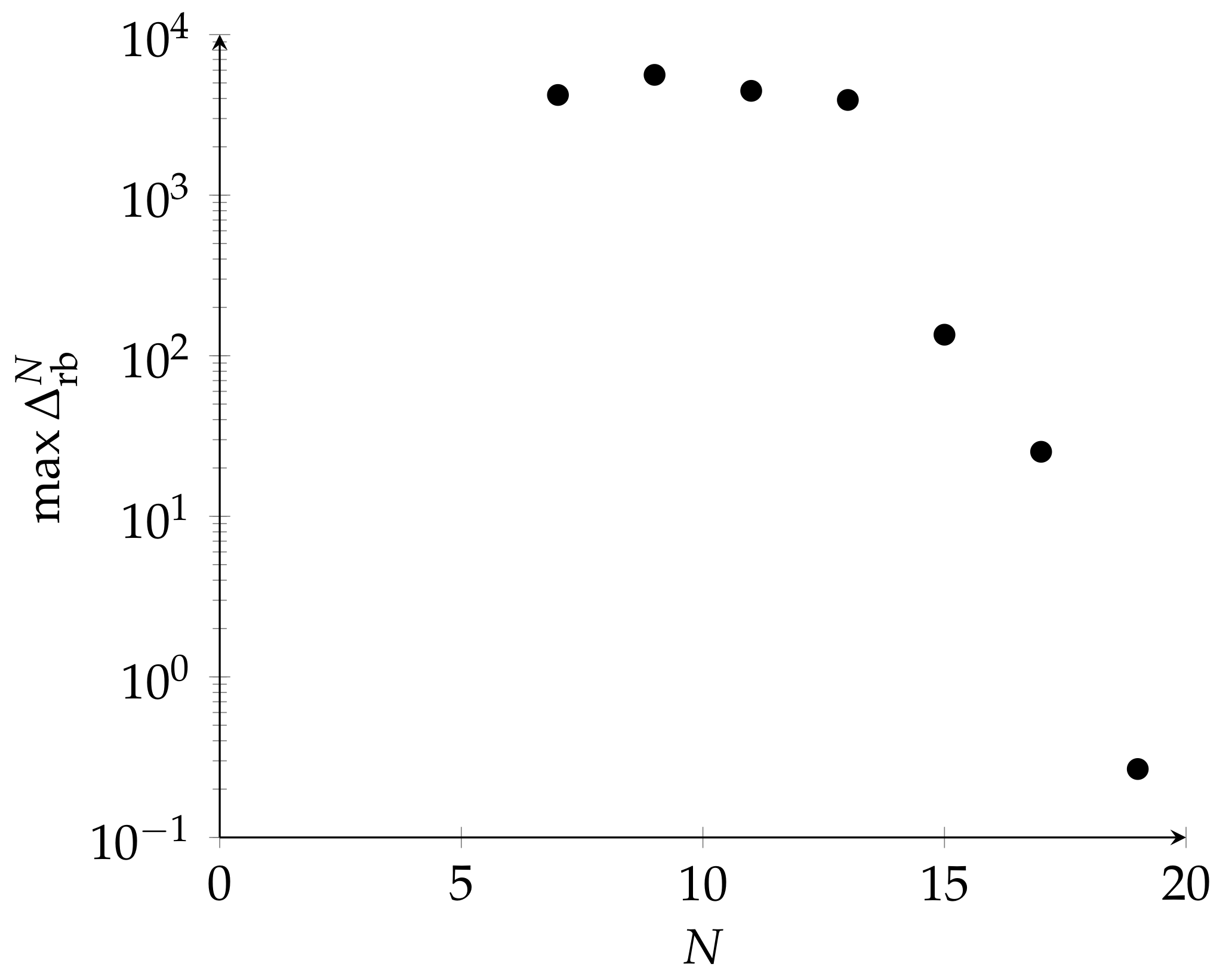
Mathematics, Free Full-Text
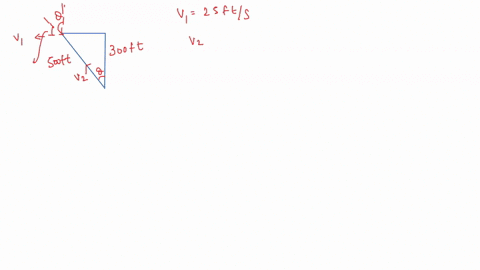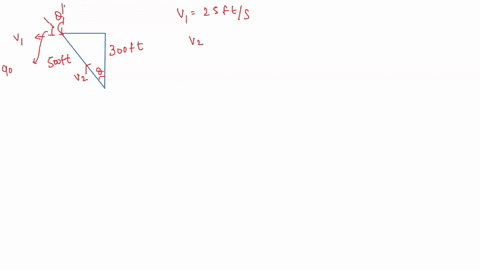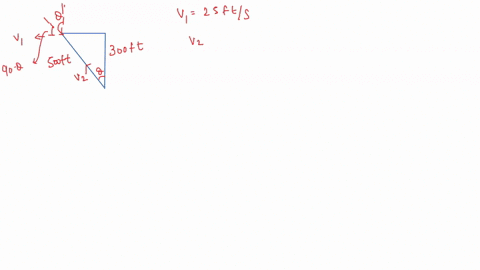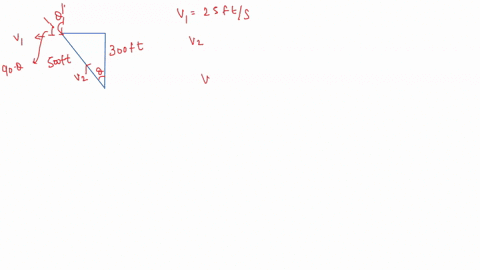
SOLVED: In the following sequence of problems, we will start the proof of the Four-Square Theorem conjectured in the third century by Diophantus and proven by Lagrange in 1770 (since it took

SOLVED: 8.35 (Lagrange's Four-Square Theorem) If n is a natural number, it can be expressed as the sum of four squares. A lattice in 4-space is a set of the form (x,y,z,w)

SOLVED: Let 0 be a square-free integer. Consider Z[v-d] = a + Vedb : a,b ∈ Z. For d = 1, this is exactly the ring Z[i] of Gaussian integers. Show that
Recomendado para você
-
Lagrange's four-square theorem - Wikipedia31 dezembro 2024
-
 Lagrange's four-square theorem, polynomials, diophantine equations, prime numbers31 dezembro 2024
Lagrange's four-square theorem, polynomials, diophantine equations, prime numbers31 dezembro 2024 -
 SOLVED: Theorem 8.35 (Lagrange's Four-Square Theorem) then n can be expressed as the sum If n is a number; of four squares: natural lattice A in 4-space is a set of the31 dezembro 2024
SOLVED: Theorem 8.35 (Lagrange's Four-Square Theorem) then n can be expressed as the sum If n is a number; of four squares: natural lattice A in 4-space is a set of the31 dezembro 2024 -
 Solved QUADRA range's Four-Square Theorem) If n is a natural31 dezembro 2024
Solved QUADRA range's Four-Square Theorem) If n is a natural31 dezembro 2024 -
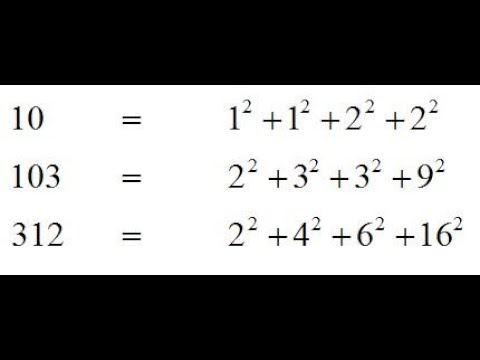 Number Theory Sums of Squares Part 7.31 dezembro 2024
Number Theory Sums of Squares Part 7.31 dezembro 2024 -
 RISIBUES 221 orem 8.35 (Lagrange's Four-Square31 dezembro 2024
RISIBUES 221 orem 8.35 (Lagrange's Four-Square31 dezembro 2024 -
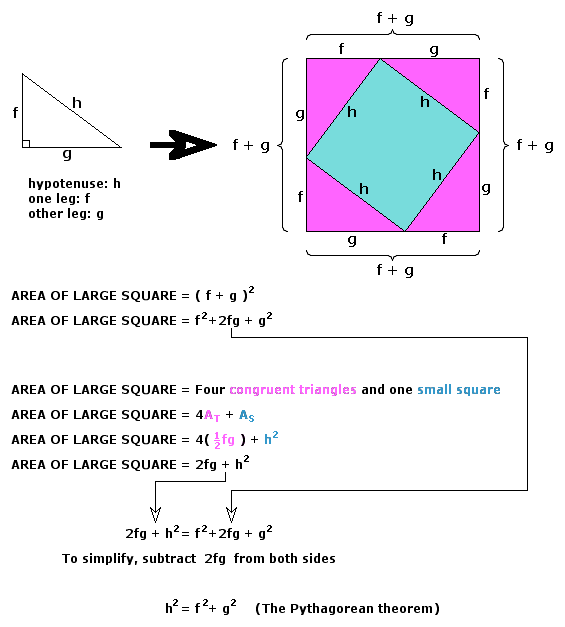 Pythagorean Theorem31 dezembro 2024
Pythagorean Theorem31 dezembro 2024 -
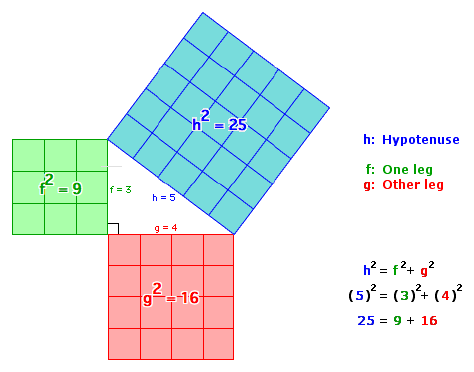 Pythagorean Theorem31 dezembro 2024
Pythagorean Theorem31 dezembro 2024 -
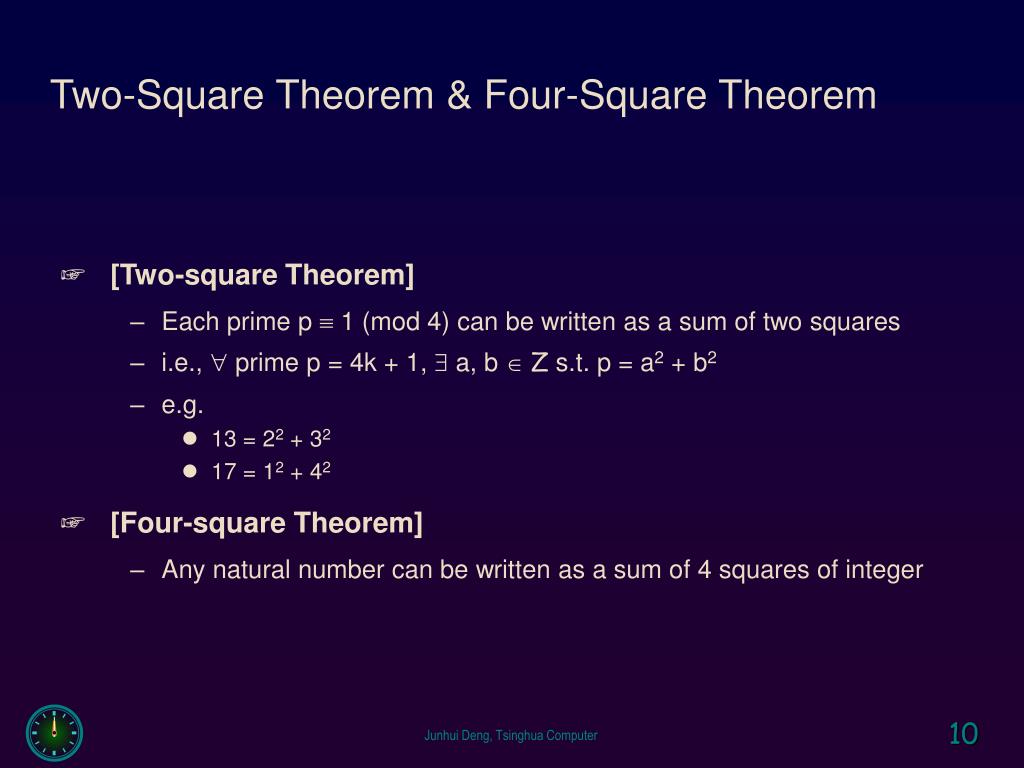 PPT - Combinatorial Geometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:488680831 dezembro 2024
PPT - Combinatorial Geometry PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:488680831 dezembro 2024 -
 1.28: Sum of Squares - Mathematics LibreTexts31 dezembro 2024
1.28: Sum of Squares - Mathematics LibreTexts31 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Jogo Horse Racing Derby Quest no Jogos 36031 dezembro 2024
Jogo Horse Racing Derby Quest no Jogos 36031 dezembro 2024 -
 Visit Campus (Full-Time MBA Program)31 dezembro 2024
Visit Campus (Full-Time MBA Program)31 dezembro 2024 -
Top Anime pack Cursors31 dezembro 2024
-
 People Stickman Playground 3D APK for Android Download31 dezembro 2024
People Stickman Playground 3D APK for Android Download31 dezembro 2024 -
 Vetores de Aliens E Ovnis Desenhados À Mão Espaçonaves Alienígenas De Desenho Animado Bonito Doodles E Lettering Vector Ilustração Em Fundo De Lousa e mais imagens de Alienígena - iStock31 dezembro 2024
Vetores de Aliens E Ovnis Desenhados À Mão Espaçonaves Alienígenas De Desenho Animado Bonito Doodles E Lettering Vector Ilustração Em Fundo De Lousa e mais imagens de Alienígena - iStock31 dezembro 2024 -
 Atriz de “Barrados no Baile” descobre motivo de filhos ficarem sempre doentes31 dezembro 2024
Atriz de “Barrados no Baile” descobre motivo de filhos ficarem sempre doentes31 dezembro 2024 -
 Gears 5 Gears of War - Stickers / Decals Gears Logo 2 Stickers Included31 dezembro 2024
Gears 5 Gears of War - Stickers / Decals Gears Logo 2 Stickers Included31 dezembro 2024 -
 39 Photos & High Res Pictures - Getty Images31 dezembro 2024
39 Photos & High Res Pictures - Getty Images31 dezembro 2024 -
 Eyes: Scary Thriller Mod APK 6.1.60 (Menu, Unlocked, Immortality)31 dezembro 2024
Eyes: Scary Thriller Mod APK 6.1.60 (Menu, Unlocked, Immortality)31 dezembro 2024 -
 Riku Dola31 dezembro 2024
Riku Dola31 dezembro 2024
