Stimulation–Inhibition of Protein Release from Alginate Hydrogels Using Electrochemically Generated Local pH Changes
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 22 setembro 2024


Smart/stimuli-responsive hydrogels: Cutting-edge platforms for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications - ScienceDirect

Stimuli‐responsive delivery of therapeutics for diabetes treatment - Yu - 2016 - Bioengineering & Translational Medicine - Wiley Online Library

A) Schematics of the DNA deposition on the positively charged

Full article: Platinum-based drugs and hydrogel: a promising anti-tumor combination

Programming hydrogel adhesion with engineered polymer network topology

Stimulation–Inhibition of Protein Release from Alginate Hydrogels Using Electrochemically Generated Local pH Changes
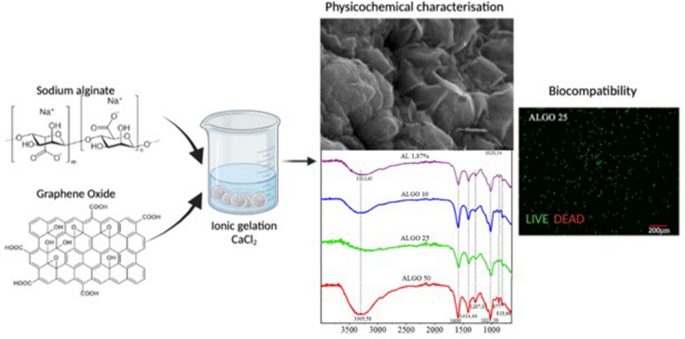
Encapsulation of beta-pancreatic cells in a hydrogel based on alginate and graphene oxide with high potential application in the diabetes treatment

Interaction Pathways and Structure–Chemical Transformations of Alginate Gels in Physiological Environments

Electrochemically controlled drug-mimicking protein release from iron- alginate thin-films associated with an electrode.
Recent advances in various stimuli-responsive hydrogels: from synthetic designs to emerging healthcare applications - Materials Chemistry Frontiers (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2QM00469K

Full article: Bacterial cellulose as a potential biopolymer for wound care. A review

Cell encapsulation - Wikipedia

Stimulation–Inhibition of Protein Release from Alginate Hydrogels Using Electrochemically Generated Local pH Changes

A) Schematically shown swelling−shrinking of the alginate hydrogel
Recomendado para você
-
 Long Dong Silver music, videos, stats, and photos22 setembro 2024
Long Dong Silver music, videos, stats, and photos22 setembro 2024 -
 The Long Song - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024
The Long Song - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024 -
 Song Dong - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024
Song Dong - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024 -
 Cherish (The Association song) - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024
Cherish (The Association song) - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024 -
It's a Long Way to Tipperary - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024
-
 Footloose (song) - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024
Footloose (song) - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024 -
 Sunset Song - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024
Sunset Song - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024 -
 Queendom (song) - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024
Queendom (song) - Wikipedia22 setembro 2024 -
 Florida Kilos (song), Lana Del Rey Wiki22 setembro 2024
Florida Kilos (song), Lana Del Rey Wiki22 setembro 2024 -
The 25 Highest-Trending K-Pop Artists Right Now, According To Wikipedia - Koreaboo22 setembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Brasil x Peru Como assistir ao jogo da Seleção nas Eliminatórias22 setembro 2024
Brasil x Peru Como assistir ao jogo da Seleção nas Eliminatórias22 setembro 2024 -
 Generation 20: The Gate of Sanctuary - Mabinogi World Wiki22 setembro 2024
Generation 20: The Gate of Sanctuary - Mabinogi World Wiki22 setembro 2024 -
 Boarding Patrol: Leagues of Votann W40k Box Set - Features, Models, and Offers!22 setembro 2024
Boarding Patrol: Leagues of Votann W40k Box Set - Features, Models, and Offers!22 setembro 2024 -
IGN - Invincible Season 1 on Prime Video is great, thanks22 setembro 2024
-
 Tenjou Tenge: The Ultimate Fight (Tenjho Tenge: The Ultimate Fight)22 setembro 2024
Tenjou Tenge: The Ultimate Fight (Tenjho Tenge: The Ultimate Fight)22 setembro 2024 -
NextDoor Super Store22 setembro 2024
-
 Hot Wheels Monster Trucks Live Glow Party22 setembro 2024
Hot Wheels Monster Trucks Live Glow Party22 setembro 2024 -
 ZORO LUTA CONTRA FUJITORA 🇧🇷 (Dublado PT-BR), One Piece: Stampede22 setembro 2024
ZORO LUTA CONTRA FUJITORA 🇧🇷 (Dublado PT-BR), One Piece: Stampede22 setembro 2024 -
 Bloodborne may have a finished but unreleased PC version - Dexerto22 setembro 2024
Bloodborne may have a finished but unreleased PC version - Dexerto22 setembro 2024 -
Rosario Central - Platense, 17.12.2023 - H2H stats, results, odds22 setembro 2024



