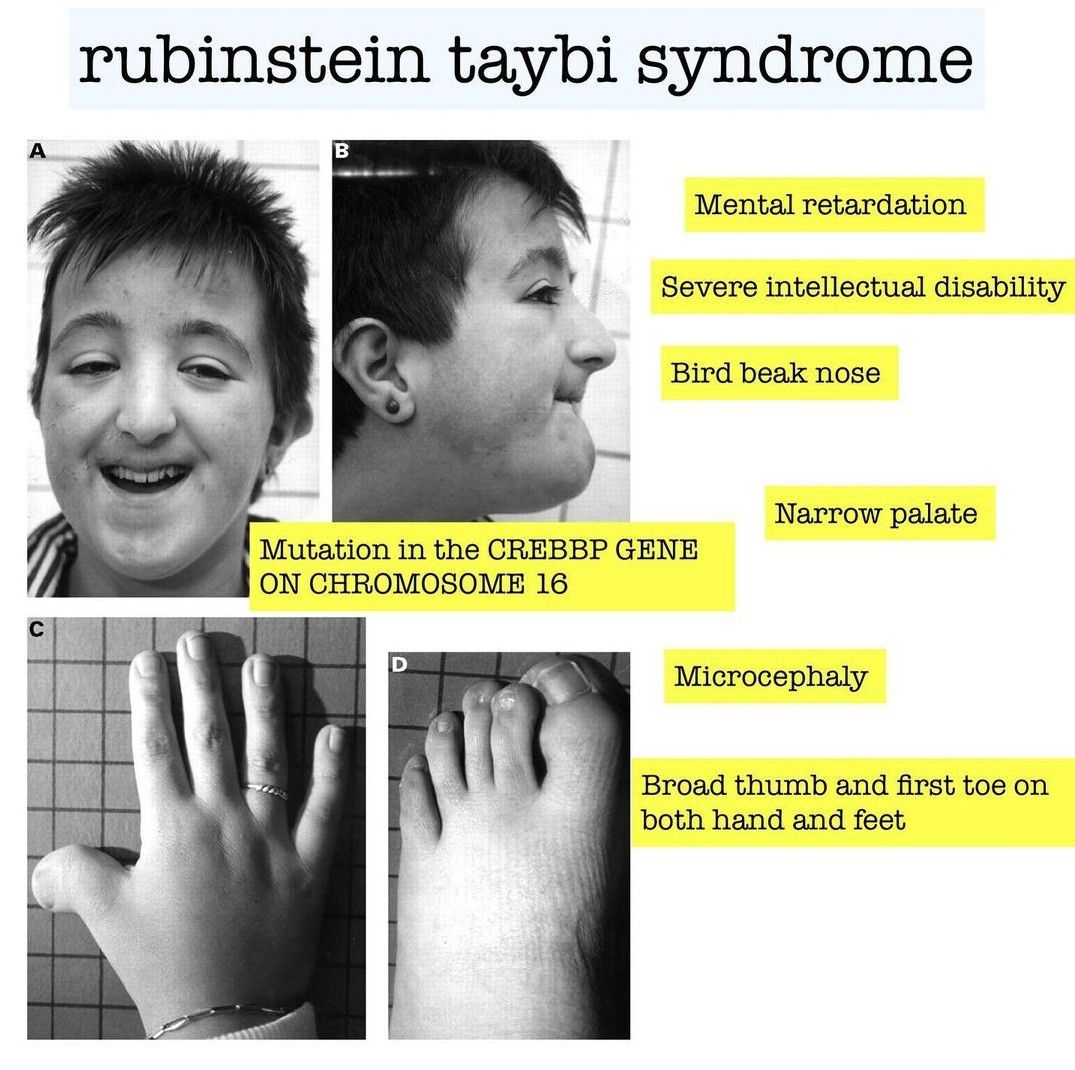
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a Saudi boy with distinct features
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 10 novembro 2024
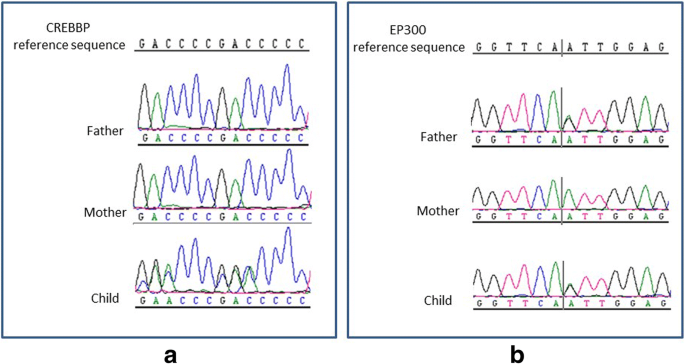
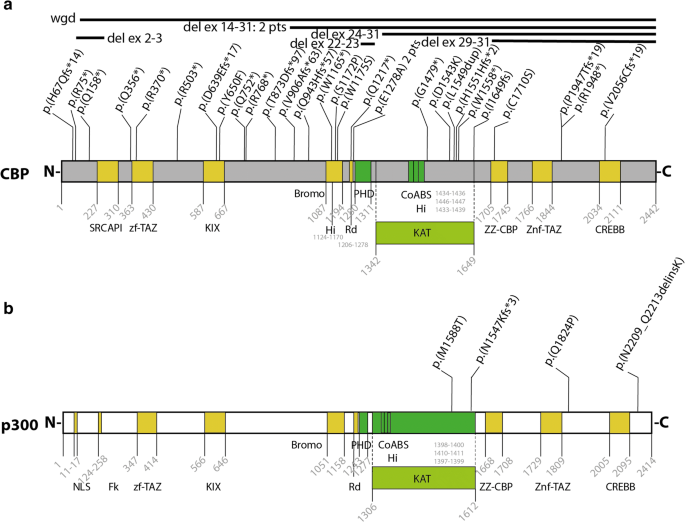
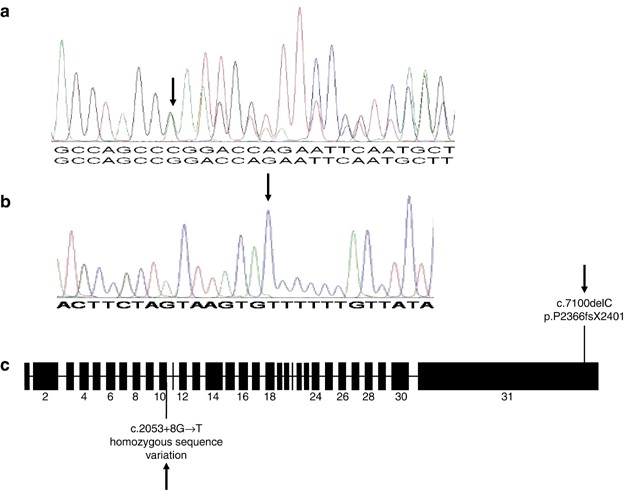
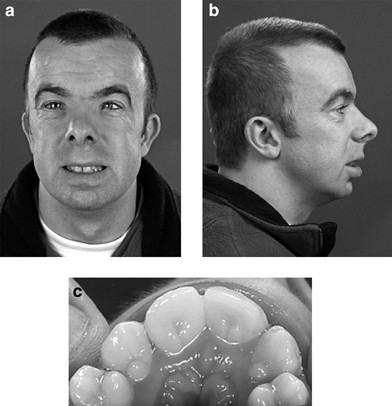
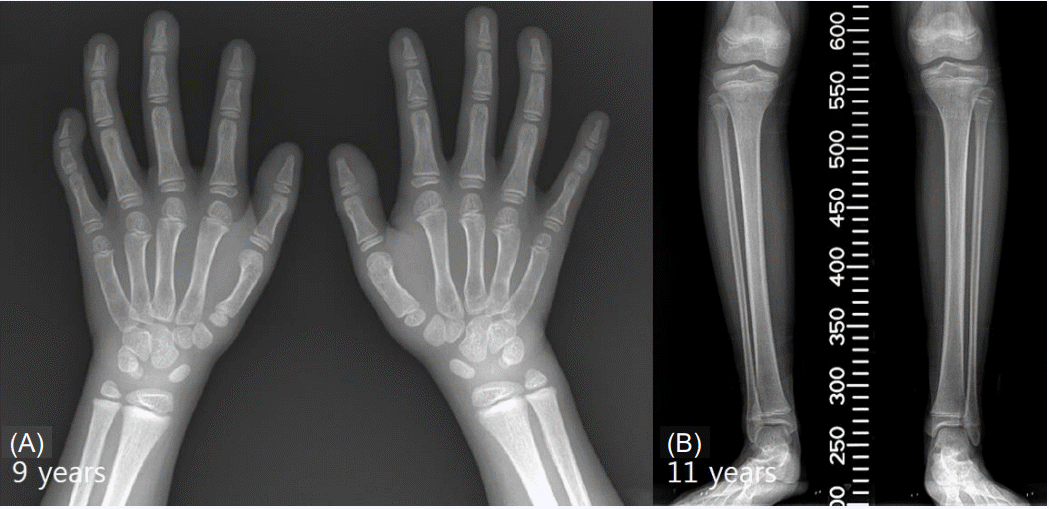
Background Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS) Type 1 (OMIM 180849) is characterized by three main features: intellectual disability; broad and frequently angulated thumbs and halluces; and characteristic facial dysmorphism. Case presentation We report on a Saudi boy with RSTS Type 1 and the following distinct features: a midline notch of the upper lip, a bifid tip of the tongue, a midline groove of the lower lip, plump fingers with broad / flat fingertips, and brachydactyly. The child was found to be heterozygous in the CREBBP gene for a sequence variant designated c.4963del, which is predicted to result in premature protein termination p.Leu1655Cysfs*89. The child and his father were also found to be heterozygous in the EP300 gene for a sequence variant designated c.586A > G, which is predicted to result in the amino-acid substitution p.Ile196Val. Conclusion Our report expands the clinical spectrum of RSTS to include several distinct facial and limb features. The variant of the CREBBP gene is known to be causative of RSTS Type 1. The variant in the EP300 gene is benign since the father carried the same variant and exhibited no abnormalities. However, functional studies are required to investigate if this benign EP300 variant influences the phenotype in the presence of disease-causing CREBBP gene mutations.

Expanding the genotypic and phenotypic spectrum in a diverse cohort of 104 individuals with Wiedemann-Steiner syndrome. - Abstract - Europe PMC
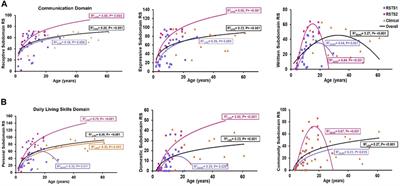
Frontiers Behavioral and neuropsychiatric challenges across the lifespan in individuals with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome

PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a Saudi boy with distinct features and variants in both the CREBBP and EP300 genes: A case report
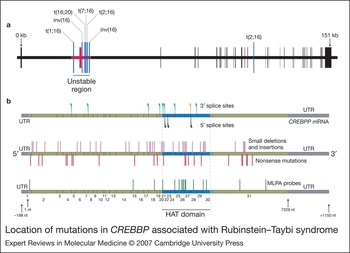
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: clinical and molecular overview, Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine
Prevalence of Immunological Defects in a Cohort of 97 Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome Patients

rubinstein-taybi syndrome adults - Google Search

PDF] Chromosome 16p13.3 Contiguous Gene Deletion Syndrome including the SLX4, DNASE1, TRAP1, and CREBBP Genes Presenting as a Relatively Mild Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome Phenotype: A Case Report of a Saudi Boy
Confirmation of EP300 gene mutations as a rare cause of Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome European Journal of Human Genetics
apem :: Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism

PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome medical guidelines

Patient 1 showing a mild RTS variant (incomplete RTS). (A, B) Note

Low bone mineral density on DXA and slipped capital femoral epiphysis as rare presentation in a child with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome
Recomendado para você
-
 Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: Behavior10 novembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: Behavior10 novembro 2024 -
Rubinstein Taybi Syndrome - MEDizzy10 novembro 2024
-
Rubenstein-Taybi Syndrome April is diagnosed with Rubinstein10 novembro 2024
-
 Adaptive (Living) Skills10 novembro 2024
Adaptive (Living) Skills10 novembro 2024 -
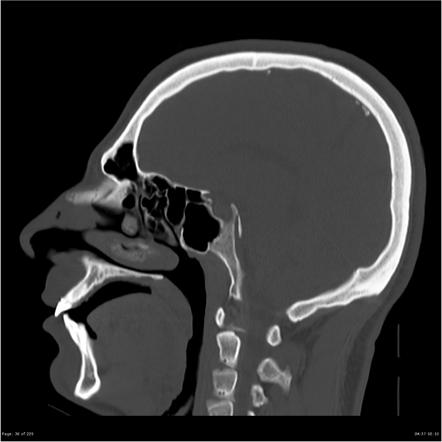 Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome Radiology Reference Article10 novembro 2024
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome Radiology Reference Article10 novembro 2024 -
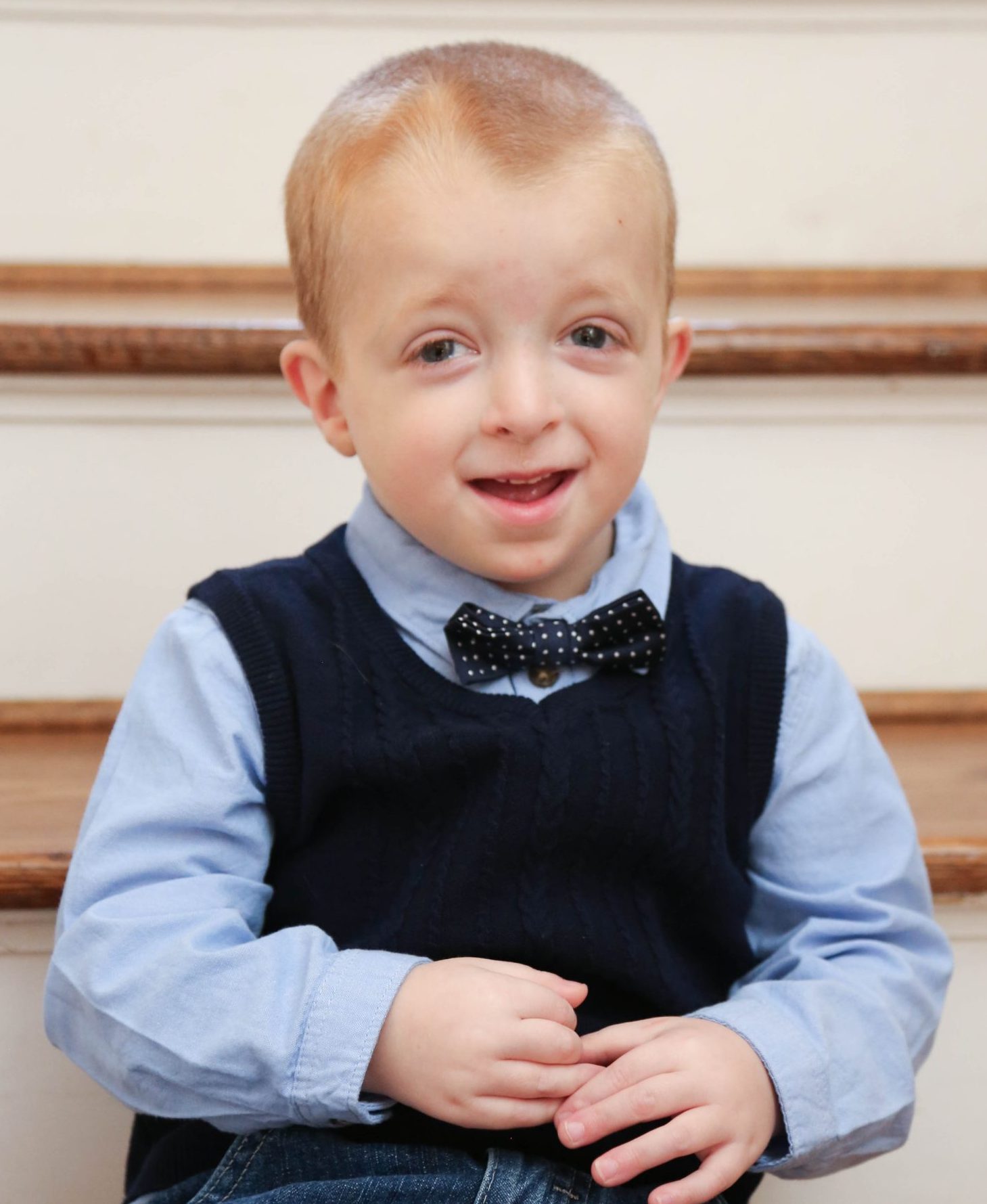 The Ridenour Family - RareKC10 novembro 2024
The Ridenour Family - RareKC10 novembro 2024 -
Rubinstein Taybi California10 novembro 2024
-
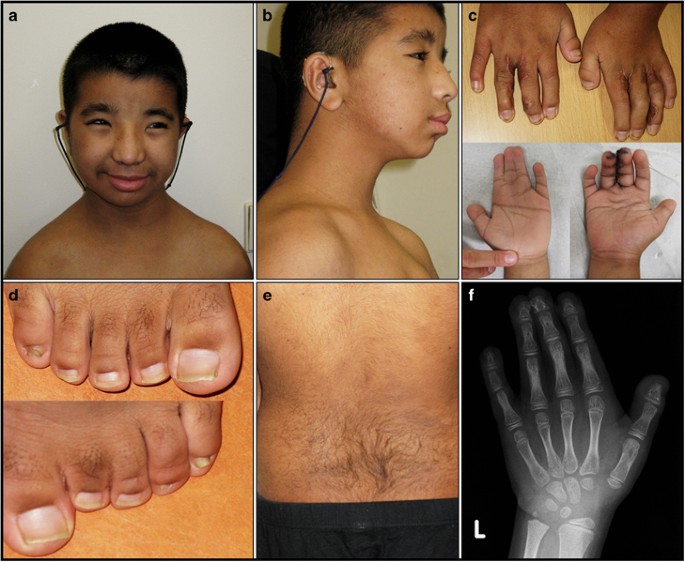 Mosaic CREBBP mutation causes overlapping clinical features of10 novembro 2024
Mosaic CREBBP mutation causes overlapping clinical features of10 novembro 2024 -
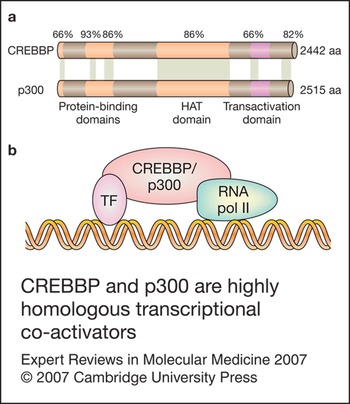 Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: clinical and molecular overview, Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine10 novembro 2024
Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: clinical and molecular overview, Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine10 novembro 2024 -
 Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: delineation of the phenotype of the first patients carrying mutations in EP30010 novembro 2024
Genetic heterogeneity in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: delineation of the phenotype of the first patients carrying mutations in EP30010 novembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Pin em Tomo-chan onnanoko!10 novembro 2024
Pin em Tomo-chan onnanoko!10 novembro 2024 -
 Horizon: Will You Need to Play Frozen Wilds Before Forbidden West?10 novembro 2024
Horizon: Will You Need to Play Frozen Wilds Before Forbidden West?10 novembro 2024 -
 Who is Benoit Badiashile? Chelsea's new centre-back star10 novembro 2024
Who is Benoit Badiashile? Chelsea's new centre-back star10 novembro 2024 -
 ROBLOX PIN CRACKER - Payhip10 novembro 2024
ROBLOX PIN CRACKER - Payhip10 novembro 2024 -
Quadro de recados para aniversário Naruto. - Convite em Vídeo10 novembro 2024
-
 One Piece: The World Government's Buster Call, Explained10 novembro 2024
One Piece: The World Government's Buster Call, Explained10 novembro 2024 -
Wavy Black Hair's Code & Price - RblxTrade10 novembro 2024
-
 An APPLe Knight (and Regulus) by @GeLinzzz : r/Reverse199910 novembro 2024
An APPLe Knight (and Regulus) by @GeLinzzz : r/Reverse199910 novembro 2024 -
 Star Fox 64 - IGN10 novembro 2024
Star Fox 64 - IGN10 novembro 2024 -
![Stream The Weeknd - Sacrifice (m1k4 Remix) [Free Download] by m1k4](https://i1.sndcdn.com/artworks-yfMVm2c1E5yuL8yc-qWNG6A-t500x500.jpg) Stream The Weeknd - Sacrifice (m1k4 Remix) [Free Download] by m1k410 novembro 2024
Stream The Weeknd - Sacrifice (m1k4 Remix) [Free Download] by m1k410 novembro 2024